Optiflow를 사용하여 환자의
치료 강화 감소
HFNC, HFOT, NHF, HF...
이 요법에 많은 약어가 사용되었지만, 이 요법 전달 방법의 명칭으로서 단연 두드러진 하나는 Optiflow입니다.
Fisher & Paykel Healthcare의 Optiflow NHF 요법은 이 분야의 최선두에 있고 수많은 간행물에
나와 있으며 NEJM 및 JAMA와 같은 권위 있는 저널에 게재되어 있습니다.
Optiflow NHF 요법을 최일선 치료법(삽관 전 및 발관 후)으로 사용하면
“중증도 곡선 상에서의 상승”을 줄일 수 있어서 환자’ 결과가 개선되고 치료 비용이 절감됩니다.
Fisher & Paykel Healthcare의 Optiflow NHF 요법은 이 분야의 최선두에 있고 수많은 간행물에
나와 있으며 NEJM 및 JAMA와 같은 권위 있는 저널에 게재되어 있습니다.
Optiflow NHF 요법을 최일선 치료법(삽관 전 및 발관 후)으로 사용하면
“중증도 곡선 상에서의 상승”을 줄일 수 있어서 환자’ 결과가 개선되고 치료 비용이 절감됩니다.
“NHF는 더 많은 급성
환자의 삽관 필요성을 크게 감소시켰습니다.”
(표준 O2 및 NIV, PaO2:FiO2 ≤ 200 mmHg과 비교하였을 때).
Optiflow는 어떻게 작용합니까?
작용 메커니즘
Optiflow NHF 요법을 사용하면 유량과 FiO2를 환자의 필요에 맞게 독립적으로 적정할 수 있습니다. 작용 메커니즘이 일반적 요법의 작용 메커니즘과 다르기 때문에 그로 인한 생리학적 효과와 임상 결과도 다릅니다.
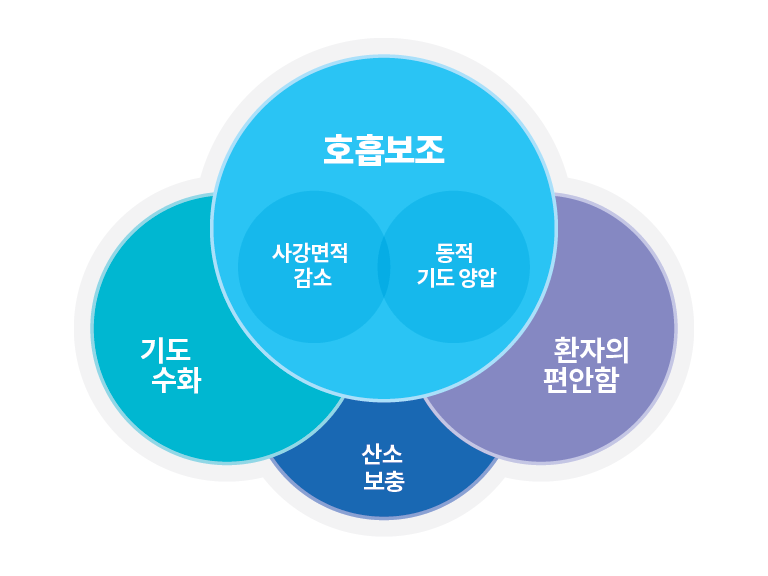
Optiflow NHF 요법의 작용 메커니즘은 다음과 같습니다.
- 호흡보조(사강의 감소 및
Dynamic 기도 양압의 전달을 통한) - 기도 수화
- 환자의 편안함
- 산소 보충(필요한 경우)
이러한 메커니즘은 호흡수 감소, 산소 공급 개선, 이산화탄소 농도 감소 및 점액 청소율 개선과 같은 생리학적 효과에 기여합니다.
임상 연구에 따르면 Optiflow NHF 요법은 치료 강화를 줄이고 사망률을 낮추며 증상 완화를 개선할 수 있습니다.
참고: 비강 고유량에 대한 위의 작용 메커니즘은 Optiflow 비강 캐뉼라 인터페이스를 통한 전달에 적용됩니다. 작용 메커니즘은 고유량이 기관절개를 통해 전달될 때, 또는 마스크 인터페이스 어댑터를 통해서 전달될 때 달라집니다.
주요 작용 메커니즘에 대해 더 알고 싶습니까? 아래의 동영상을 보십시오.
Airvo 2 시스템
2~60L/분의 유량에서, AIRVO 2는 ED 및 ICU에서부터 일반 병실을 거쳐 자택에 이르는 전체 연속적 치료 과정에 사용할 수 있는 독립형 비강 고유량 시스템입니다.
MR850 시스템
MR850 가습기는 전체 F&P Respiratory Care Continuum™에 걸쳐 모든 종류의 Fisher & Paykel Healthcare 요법에 사용됩니다.
참조 문헌
- Frat JP, Thille AW, Mercat A, Girault C, Ragot S, Perbet S et al. High-Flow Oxygen through Nasal Cannula in Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(23):2185–96.
- Hernández G, Vaquero C, González P, Subira C, Frutos-Vivar F, Rialp G et al. Effect of Postextubation High-Flow Nasal Cannula vs Conventional Oxygen Therapy on Reintubation in Low-Risk Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. (Apr) 2016; 315(13):1354–61.
- Stéphan F, Barrucand B, Petit P, Rézaiguia-Delclaux S, Médard A, Delannoy B et al. High-Flow Nasal Oxygen vs Noninvasive Positive Airway Pressure in Hypoxemic Patients After Cardiothoracic Surgery: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2015; 13(23):2331–9.
호흡수 감소
- Sztrymf B, Messika J, Bertrand F, Hurel D, Leon R, Dreyfuss D et al. Beneficial effects of humidified high flow nasal oxygen in critical care patients: a prospective pilot study. Intensive Care Med. 2011; 37(11):1780–6.
- Corley A, Caruana LR, Barnett AG, Tronstad O, Fraser JF. Oxygen delivery through high-flow nasal cannulae increase end-expiratory lung volume and reduce respiratory rate in post-cardiac surgical patients. Br J Anaesth. 2011; 107(6):998–1004.
- Roca O, Riera J, Torres F, Masclans JR. High-Flow Oxygen Therapy in Acute Respiratory Failure. Respir Care. 2010; 55(4):408–13
- Lenglet H, Sztrymf B, Leroy C, Brun P, Dreyfuss D, Ricard JD. Humidified High Flow Nasal Oxygen During Respiratory Failure in the Emergency Department: Feasibility and Efficacy. Respir Care. 2012; 57(11):1873–8.
- Rittayamai N, Tscheikuna J, Rujiwit P. High-Flow Nasal Cannula Versus Conventional Oxygen Therapy After Endotracheal Extubation: A Randomized Crossover Physiologic Study. Respir Care. 2014; 59(4): 485–90.
- Roca O, Pérez-Terán P, Masclans JR, Pérez L, Galve E, Evangelista A et al. Patients with New York Heart Association class III heart failure may benefit with high flow nasal cannula supportive therapy: High flow nasal cannula in heart failure. J Crit Care. 2013; 28(5):741–6.
- Peters S, Holets S, Gay P. High-Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy in Do-Not-Intubated Patients with Hypoxemic Respiratory Distress. Respir Care. 2013; 58(4): 597-600.
Improved oxygenation
- Ritchie JE, Williams AB, Gerard C, Hockey H. Evaluation of a humidified nasal high flow oxygen system, using oxygraphy, capnography and measurement of upper airway pressures. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2011; 39(6):1103–10.
- Masclans JR, Roca O. High-Flow Oxygen Therapy in Acute Respiratory Failure. Clin Pulm Med. 2012; 19(3):127–30.
- Peters S, Holets S, Gay P. High-Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy in Do-Not-Intubated Patients with Hypoxemic Respiratory Distress. Respir Care. 2013; 58(4): 597–600.
- Sztrymf B, Messika J, Bertrand F, Hurel D, Leon R, Dreyfuss D et al. Beneficial effects of humidified high flow nasal oxygen in critical care patients: a prospective pilot study. Intensive Care Med. 2011; 37(11):1780–6.
- Corley A, Caruana LR, Barnett AG, Tronstad O, Fraser JF. Oxygen delivery through high-flow nasal cannulae increase end-expiratory lung volume and reduce respiratory rate in post-cardiac surgical patients. Br J Anaesth. 2011; 107(6):998–1004.
- Roca O, Riera J, Torres F, Masclans JR. High-Flow Oxygen Therapy in Acute Respiratory Failure. Respir Care. 2010; 55(4):408–13.
- Lucangelo U, Vassallo FG, Marras E, Ferluga M, Beziza E, Comuzzi L et al. High-Flow Nasal Interface Improves Oxygenation in Patients Undergoing Bronchoscopy. Crit Care Res Pract. 2012; (12):1–6.
이산화탄소 농도 감소
- Möller W, Celik G, Feng S, Bartenstein P, Meyer G, Eickelberg O et al. Nasal high flow clears anatomical deadspace in upper airway models. J Appl Physiol. 2015; 118:1525–32.
- Mündel T, Feng S, Tatkov S, Schneider H. Mechanisms of nasal high flow on ventilation during wakefulness and sleep. J Appl Physiol. 2013; 114:1058–65.
- Jeong JH, Kim DH, Kim SC, Kang C, Lee SH, Kang TS et al. Changes in arterial blood gases after use of high-flow nasal cannula therapy in the ED. Am J Emerg Med. 2015;3(10):1344–9.
점액 청소 효과 개선
- Hasani A, Chapman TH, McCool D, Smith RE, Dilworth JP, Agnew JE. Domiciliary humidification improves lung mucociliary clearance in patients with bronchiectasis. Chron Respir Dis. 2008; 5(2):81–6.
치료 강화 감소
- Frat JP, Thille AW, Mercat A, Girault C, Ragot S, Perbet S et al. High-Flow Oxygen through Nasal Cannula in Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(23):2185–96.
- Hernández G, Vaquero C, González P, Subira C, Frutos-Vivar F, Rialp G et al. Effect of Postextubation High-Flow Nasal Cannula vs Conventional Oxygen Therapy on Reintubation in Low-Risk Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. (Apr) 2016; 315(13):1354–61.
- Hernández G, Vaquero C, Colinas L, Cuena R, González P, Canabal A et al. Effect of Postextubation High-Flow Nasal Cannula vs Noninvasive Ventilation on Reintubation and Postextubation Respiratory Failure in High-Risk Patients. JAMA. (Oct) 2016; 316(15):1565–74.
- Stéphan F, Barrucand B, Petit P, Rézaiguia-Delclaux S, Médard A, Delannoy B et al. High-Flow Nasal Oxygen vs Noninvasive Positive Airway Pressure in Hypoxemic Patients After Cardiothoracic Surgery: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2015; 13(23):2331-9.
사망률 저하
- Frat JP, Thille AW, Mercat A, Girault C, Ragot S, Perbet S et al. High-Flow Oxygen through Nasal Cannula in Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(23):2185–96.
증상 완화 개선
- Frat JP, Thille AW, Mercat A, Girault C, Ragot S, Perbet S et al. High-Flow Oxygen through Nasal Cannula in Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(23):2185–96.
- Roca O, Riera J, Torres F, Masclans JR. High-Flow Oxygen Therapy in Acute Respiratory Failure. Respir Care. 2010; 55(4):408-13.
- Lenglet H, Sztrymf B, Leroy C, Brun P, Dreyfuss D, Ricard JD. Humidified High Flow Nasal Oxygen During Respiratory Failure in the Emergency Department: Feasibility and Efficacy. Respir Care. 2012; 57(11):1873-8
- Frat JP, Thille AW, Mercat A, Girault C, Ragot S, Perbet S et al. High-Flow Oxygen through Nasal Cannula in Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(23):2185–96.
- Hernández G, Vaquero C, González P, Subira C, Frutos-Vivar F, Rialp G et al. Effect of Postextubation High-Flow Nasal Cannula vs Conventional Oxygen Therapy on Reintubation in Low-Risk Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. (Apr) 2016; 315(13):1354–61.
- Hernández G, Vaquero C, Colinas L, Cuena R, González P, Canabal A et al. Effect of Postextubation High–Flow Nasal Cannula vs Noninvasive Ventilation on Reintubation and Postextubation Respiratory Failure in High–Risk Patients. JAMA. (Oct) 2016; 316(15):1565–74.